Safety Measures on Narrow Bridge
What is a narrow bridge?
Any bridge width less than XX mtrs of the standard width of carriageway specified in the standard and specification shall be considered a restricted-width bridge. It becomes a dangerous and risky area in a highway project. These narrow bridges pose potential hazards to users.
The following content provides an overview of the required safety measures on narrow bridge. The CA provisions require their implementation on these narrow bridges. Implementing these measures is necessary to ensure road user safety. Its application is critical during the project’s augmentation phase and the O&M phase.
The content features draft sentences, examples, and recommendations related to the titled subject. Below is a brief summary of the letter’s subject and content matter.
- A letter to the concessionaire for the implementation of safety measures on the narrow bridge. This is to aid road user safety on the project highway during the O&M phase. This appeal is to the concessionaire as per the contractual regulations of the CA.
- Suggestions for safety enhancements for the restricted-width, narrow bridges are included.
- Urge the concessionaire for compliance on measures to implement on or at a narrow bridge. During the development and construction phases of the project,.
- Additionally, the content focuses on the concession agreement’s related contractual provisions.
- This content also contains guidelines to be considered for structures, especially the Narrow Bridge, during the development and construction stages.
Safety Measures on Narrow Bridge Letter 1:
Implementation of safety measures on the narrow bridge.
Here’s a sample draft letter format for the concessionaire. To clearly indicate the submission of a compliance report for important safety implementations. CA regulations require that these safety enforcements be placed at a narrow bridge (rather than widening the bridge) to reduce the risks associated with a narrow bridge. This implementation aims to enhance road user safety on the project highway during the operation and maintenance phases. And also request compliance with concession regulations.
|
To The Concessionaire, Subject: Safety measures to install on or at a narrow bridge. Dear Sir, During the site inspection, it was observed that there were no safety measures on the narrow bridge or restricted carriageway width. Additionally, the narrow bridge lacks any warning safety signs or elements that could alert and secure the user, thereby preventing possible collisions.
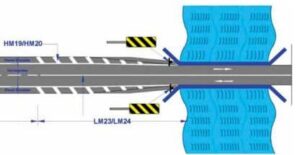
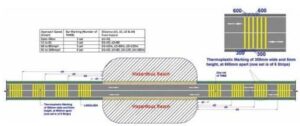
As per Article 18 safety requirements of the CA, ”The concessionaire shall comply with the provisions of this agreement, applicable laws, and applicable permits and conform to the good industry practices for securing the safety of the user. In particular, the concessionaire shall develop, implement, and administer a surveillance and safety programme for providing a safe environment on or about the project highway and shall comply with the safety requirements set forth in Schedule L (”Safety Requirements”). In this regard, it is suggested that proactive safety measures be put in place. Such as hatching on the paved shoulder with raised pavement edge lines or markers. Additionally, place appropriate signage in front of the narrow bridge. This will alert you to avert the collision of vehicles with the crash barrier. The taper part, also known as the nose length advanced to the narrow bridge at Km. 20+150, should be appropriately marked with hatch marks. This is as stipulated in the codal provisions of IRC 35. This measure is to illustrate and caution against the reduction in paved width and carriageway upon the narrow bridge. Important safety implementations at narrow bridges (other than widening a bridge) are crucial for reducing the hazards associated with a narrow bridge.The safety treatment recommendations for the restricted-width, narrow bridges were fundamentally similar. The only changes were in the management of the approach rail after it moved onto the bridge. Also, the addition of clear markings served as a visual help for drivers. The following safety treatment recommendations apply to restricted-width, narrow bridges.You can apply the following to either lower the likelihood of accidents or lessen their severity.
ConclusionWe explicitly instruct you to submit the compliance report for the above-cited instructions. This is in accordance with the agreement provisions to ensure a safe and smooth traffic flow on the project highway. Thank you, and we assure you of our best service at all times. [Yours Sincerely,] [Insert the name of the authorised person]. |
**********************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************
Safety Measures on Narrow Bridge Letter 2:
Measures to implement on or at a narrow bridge.
The following is a sample draft letter format for the concessionaire for measures to implement on or at a narrow bridge. These implementations occurred during the development and construction phases of the project highway. And urges a compliance request.
| To
The Concessionaire, Subject: Measures to implement on or at a narrow bridge. And requests for compliance with concessionaire regulations Dear Sir, This pertains to the subject matter discussed in the cited reference. Currently, the preparation of designs and good construction drawings for structures is in progress. We would like to draw your attention to the following, in addition to the guidelines outlined in Schedule B (Development of the Project Highway) of the concession agreement. These guidelines are crucial for the design, construction, and rehabilitation of both new and existing structures. Guidelines to be considered for structures, especially the Narrow Bridge, during the development and construction phases The following section provides a brief overview of the scope and work associated with “project structures that are newly constructed and existing to retain.” When designing and building bridges and other structures, adhere to the following guidelines:
Thank you, and we assure you of our best service at all times. [Yours Sincerely,] [Insert the name of the authorised person]. |
Safety Measures on Narrow Bridge: A note to the Visitor
Please note that the concession agreement for the DBFOT project under the PPP mode serves as an example of the aforementioned contractual conditions. For the period 2016–2018,
Afterwards, make sure to make the necessary modifications to the existing contractual conditions. Write a letter that aligns with the concession agreement applicable to the particular project.
Also read the BI and BBD letters and the NSV Report Letter: Request for Programme, Submission, Review of Observations, and Comments.
You can find various sample draft formats for highway operation and maintenance correspondence.
Safety measures on Narrow Bridge: FAQs
The team highway correspondence will update relavent FAQs shortly.